FaQ about Magnets and Services
MAGNETS
Neodymium or Ferrite Magnets, which one is the best?
This is a tough question, since the determining factor is the intended role of the magnet. Ferrite magnets, although weaker, are surely cheaper, while neodymium magnets are stronger and therefore more expensive. Read More in a dedicated article
How do you take magnets apart?
The best practice is to slide one over the other; we advise against trying to pull them apart vertically, since you may hurt yourself or damage the magnets.
How do you make magnets adhere to non-magnetic surfaces?
You can successfully use magnets on non-ferrous materials with the help of bioadhesive tape, glue or screws. You just put one magnet in place and use another of opposite polarity to make them safely stick together.
What can cause a magnet to demagnetize?
Oxidation, electric discharges and high temperatures (always follow our guidelines) are some of the main factors that can damage a magnet and cause a loss of magnetization. If you want to know more about that and learn how to properly store your magnets, you can read our complete guide: Loss of Magnetization and Demagnetization of Permanent Magnets
Quelle température un aimant peut-il supporter ?
Les aimants en néodyme standard ont une température de travail maximale de 80 °C. Ce seuil est de 250 °C pour les aimants en ferrite, 350 °C pour les aimants en SmCo et 650 °C pour les aimants en Alnico. Il existe également des aimants en néodyme spécialement traités avec des températures de travail supérieures à 100 °C. Have a look at our HEAT RESISTANT MAGNETS. You can also read our complete guide:
Aimants permanents et résistance à la chaleur: les meilleurs aimants à utiliser
Magnets for Magnetotherapy?
In Magnet Therapy the magnetic field of permanent magnets is used for many therapeutic applications. All based on the principles of Biomagnetism. Discover ourMAGNETS FOR MAGNET THERAPY or read more in our dedicated article:
AIMANTS, MAGNÉTOTHÉRAPIE ET BIOMAGNÉTISME : LE GUIDE COMPLET
Magnets for Magnet Fishing?
In Magnet Fishing, powerful Neodymium Magnets are used to recover objects from the bottom of the sea, lakes and rivers. All you need to get started is one of our MAGNETS FOR MAGNET FISHING! Read more in our dedicated article:
Specific Glue for Magnets?
Magnets come off easily when glued with regular glue, which tends to crumble. We always recommend using our two-component MAGNET GLUE. We tested many solutions but this proved to be the most effective and long-lasting glue!
How to properly store magnets?
Neodymium magnets are delicate and you shouldn’t expose them to temperatures above 80°C or humidity. Ferrite Magnets are more resistant to heat, water and corrosion.
Avoid keeping strong magnets close to each other for long periods of time. If you need to store multiple magnets together, place them in stacks facing the same way. Permanent magnets are quite fragile, strong impacts can break them or cause a in loss of performance.
Read more in our dedicated article:
LOSS OF MAGNETIZATION AND DEMAGNETIZATION OF PERMANET MAGNETS
Is it ok to use a Plastoferrite magnet as a counterpart for a Neodymium one?
We advise against such practice, since the Neodymium would make the Ferrite lose his magnetization, therefore becoming useless.
AIMANTS EN NÉODYME
What do the letters M, H, SH, UH and EH mean when referring to Magnets?
All these acronyms indicate the maximum temperature a magnet can withstand before permanently losing some of its magnetization. Une de ces lettres peut être placée après le grade de l’aimant pour indiquer sa résistance à la démagnétisation. An example for a magnet with an “M” resistance is N35M, generally means that a magnet can be used in an operating environment up to 100°C. An “H” magnet performs ok up to 120C, “SH” up to 150C, “UH” up to 180C, “EH” up to 200C, and a “TH” up to 220C. These are general specifications and other factors do play a role in coercivity decisions. 80 degrees Celsius is the standard limit (no acronym in the product page), but on request we are also able to produce magnets with higher heat resistance.
What N35, N38, N40, N42, N45, N48, N50, N52 all stand for?
These attributes stand for the magnetization grade.
It tells the adhesive force of the magnet; the higher the number after the N, the stronger the force.
Are the countersunk and adhesive tape magnets sold with both north and south polarity?
Yes they are. We always provide our customers with half and half polarities to guarantee that, no matter the final usage, the magnets can be made to stick together or against a metal surface without issues!
Do north and south polarities have the same adhesive force?
Yes, they do. The difference is so negligible, that we can safely say that the adhesive force is the same.
How are north and south polarities made?
Magnetization is obtained through an electric discharge inside the magnetizer. The side from which the electricity enters the magnet becomes the north pole, the exit side becomes the south one.
Can neodymium magnets be cut?
We advise against cutting neodymium magnets. Being made by extrusion and of powders, they are very prone to damage; moreover, the magnetization could be lost. Après avoir coupé un aimant, la polarité s’inversera à l’endroit où la coupe est effectuée.
Can you use magnets in humid environments or underwater?
Neodymium magnets rust easily, therefore it is very risky to use them in humid environments if not adequately protected. The solution to this problem is to use plastic-encased magnets or resin-coated pot magnets. On the other end Ferrite Magnets are very resistant to corrosion, oxidation and humidity.
What coatings are available?
Among our coatings you can choose between zinc, nickel, gold, and black epoxy.
If the magnet has to come in contact with the skin, you would want to opt for a zinc-coated one. This guarantees that the magnet is nickel-free. Otherwise, the differences between the two coatings are just minor and cosmetic, the nickel being shinier and smoother.
Les revêtements époxy dorés et noirs offrent une couleur différente du gris standard, mais n’améliorent pas le degré de protection.
What does “marked” mean on Magnets?
A marked magnet has a red or black dot on the relevant pole. This way the client knows the correct polarity and it becomes easier to assemble the magnets together (north against south).
Why are there magnets placed in pots like those in the magnetic system category?
Neodymium magnetic systems are specifically designed to maximize the adhesive force. Indeed, the strength of the assembled pot magnet is higher, thanks to the iron pot that redirects all the magnetic attraction towards the free side of the magnet.
Can Neodymium magnets lose their magnetism?
Under usual circumstances, neodymium magnets lose 1% of their magnetism each year. If, on the other hand, they are exposed to higher than recommended temperatures (the standard in 80 degrees Celsius), or to electric discharges (galvanic bath), they can likely lose their magnetism altogether. In a theoretical scenario where 10 magnets undergo the same stress, it is not guaranteed that all of them will become unmagnetized, but is very likely that a good portion of them will.
What temperature is safe for neodymium magnets?
Without a specific treatment, neodymium magnets can withstand a maximum temperature of 80 degrees Celsius. We are also able to produce magnets that reach 200 degrees. Please, send us a request to make sure that magnet size you are interested in is available with these custom treatments.
What is the force direction of our neodymium magnets?
Our neodymium magnets come with axial magnetization as standard.
On request we can provide different directions as well.
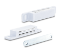
What does axial magnetization mean?
Axial magnetization means that the disc or ring is magnetized through its depth or height, and the poles are located on the flat surface. Diametrically magnetized means that the magnetic axis runs through the diameter, and the poles are located opposite along the lateral surface. Example of axial magnetized magnet:
What factors make neodymium magnets go up in price?
The price of the required raw materials fluctuates rapidly, therefore the price of the magnets in our shop can change rapidly and considerably in a short amount of time according to the current market situation.
AIMANTS EN FERRITE
What are ferrite magnets made of?
Ferrite magnets are made of two different iron alloys: with strontium or with barium.
What applications are most common for ferrite magnets?
Ferrite magnets are widely used in souvenirs and gadgets, magnet therapy and in the speaker manufactory.
How much do ferrite magnets cost?
It is a common misconception that ferrite magnets are cheaper than neodymium ones.
Having less adhesive force, in order to reach the same one as a neodymium magnet the ferrite magnet will have to be quite bigger, raising its cost.
PLASTOFERRITE
What is Plastoferrite?
Plastoferrite is a type of magnetized rubber band made of 90% barium- or strontium-ferrite and 10% of thermoplastic components.
How do you utilize Plastoferrite?
Usually it is used as fridge gasket, as support for flyscreens, as advertisement billboards, as support for lightweight but cumbersome materials, for magnetic labels, as magnetic board or as magnet for gadgets and souvenirs.
SHIPPING

How much are the shipping fees on SuperMAgneticShop?
Shipping fees are determined by the weight of the package and your shipping address. The cost will be calculated automatically at checkout.
When will my order be ready for shipping?
If you complete your order before 12:00 it will be shipped the same day; should you choose to pay with bank transfer we will wait to receive the money in our bank account before shipping the goods.
How long does it take to receive my order?
Shipping should take 24/48 hours, except for delays of the courier. Should you need the tracking number, do not hesitate to write us an email and we will gladly provide you with it.
How are the magnets packaged?
Our packages consist of recycled cardboard and pluriball. Depending on the quantity, magnets can be shipped inside envelopes or one or more boxes.